CARoLINE in the End-of-Line Test
CARoLINE has been developed for the evaluation of the assembly quality and function of electromotive vehicle components. With the help of statistical analyses and the evaluation of acoustic properties you can improve the manufacturing and assembly processes. These methods are provided by the acoustic system CARoLINE. With simple parameters, complex methods such as pulse valuation, order filter or scaling are adjustable.
Via scatter diagrams/spread patterns you can test the parameters and adapt the manufacturing process.
Impact Sound Analysis
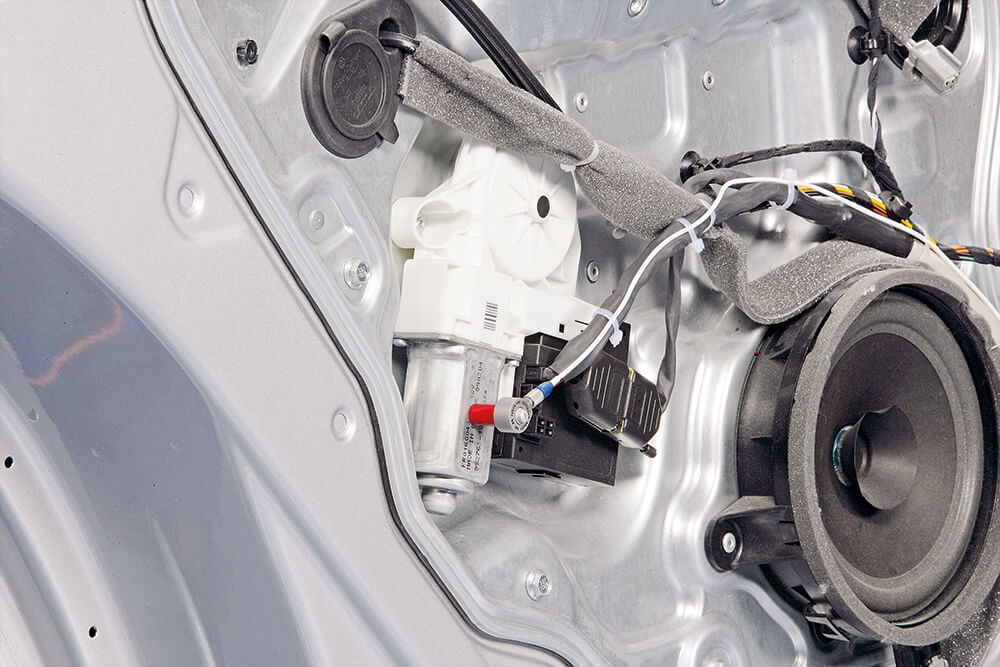
To evaluate the quality of rotating, motor-driven components in the vehicle, impact sound analyses became more and more essential. Besides the reduction of noise, it is helpful to identify noises to evaluate the quality of manufacturing.
The system for impact sound analysis consists of impact sound sensors, modules for data entry and installed evaluation software.
These sensors are attached by metallic brackets, magnets or directly to the motor-driven units under test.
GÖPEL electronic chooses the adequate sensors for impact sound measurement together with you and advises you on the integration into the equipment.

Software
The software is modularly configured. Thus, the software system is able to execute all analysis processes in parallel.
The trigger conditions and parameterization of the single calculations and evaluations are handled in the inbound data stream by the data server in parallel processes. Thus, you as the user can arrange several process steps in parallel running modules and parameterize your test procedures. An editor is available to edit the test processes.
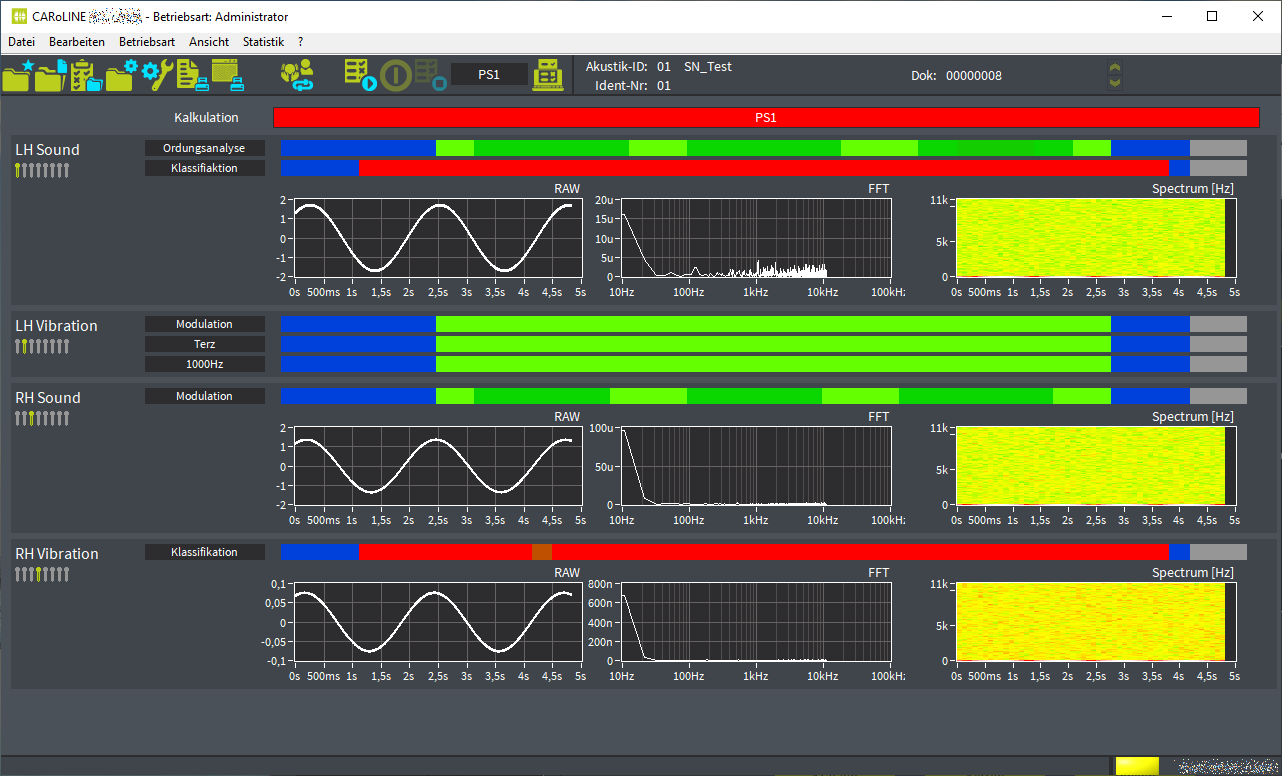 Anzeige von Rohdaten, FFT und Spektrum des Sensors pro Kanal.
Anzeige von Rohdaten, FFT und Spektrum des Sensors pro Kanal.- Status der Prüfschritte:
blau = CutOn- und CutOff-Grenzen | grau = unbenutzt | gelb = in Arbeit | grün = Ergebnis ok | rot = Ergebnis nicht in Ordnung
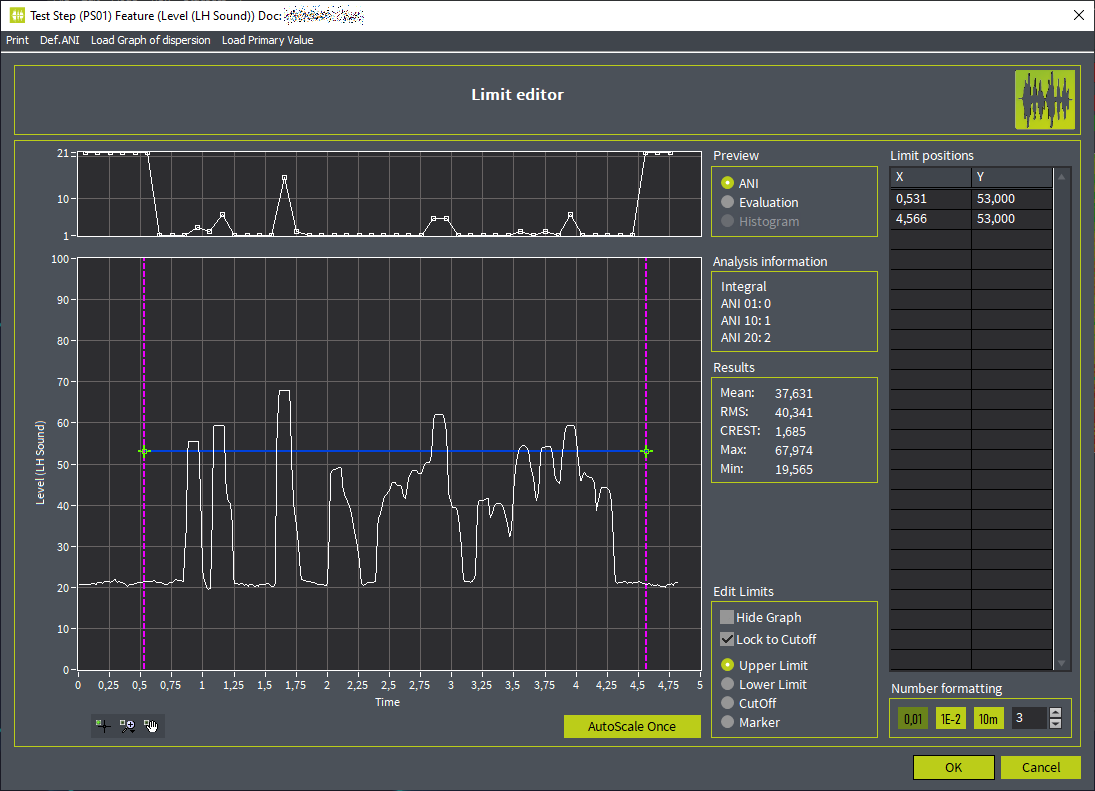 Bewertung eines zeitlichen Signals nach der Analyse
Bewertung eines zeitlichen Signals nach der Analyse - Definition von CutOn- und CutOff-Grenzen für zeitliche Eingrenzung sowie Pegelgrenzen für Eingangsdaten
- Erstellung eines Diagramms mit Häufigkeitsverteilung möglich, um Trends in Aufnahmen zu erkennen
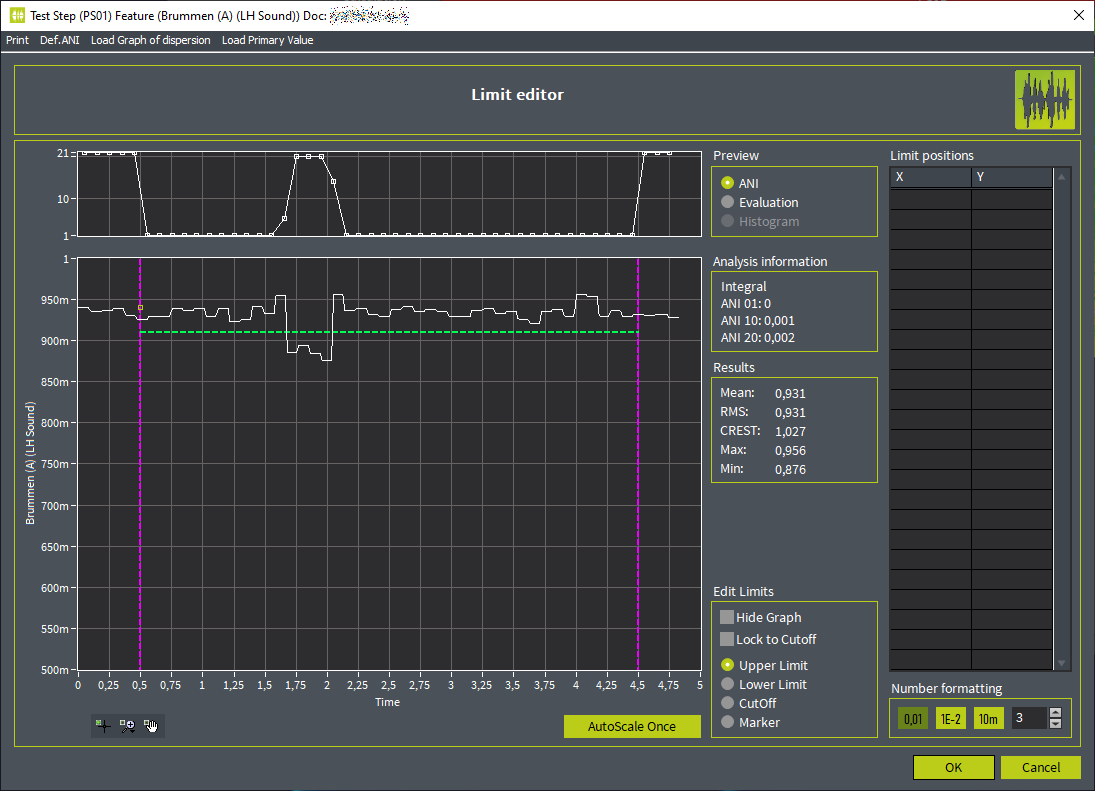 Bewertung eines Signals nach der Analyse durch ein neuronales Netz
Bewertung eines Signals nach der Analyse durch ein neuronales Netz- Definition von CutOn- und CutOff-Grenzen für zeitliche Eingrenzung der Bewertung
- Definition von Grenzen für Wahrscheinlichkeitswerte
- Erstellung eines Diagramms mit Häufigkeitsverteilung möglich, um Trends in Aufnahmen zu erkennen
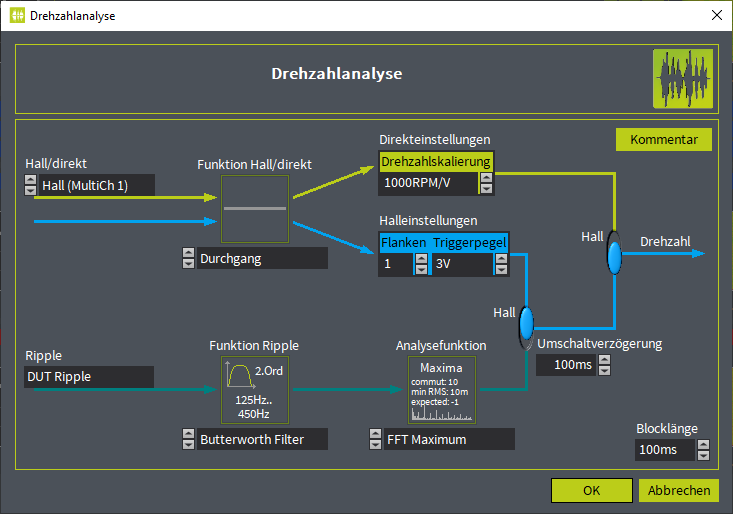 Drehzahlanalyse
Drehzahlanalyse - Definiton der Berechnung der Drehzahl
- Grundlage sind Stromripple-Signal, das Hall-Signal oder ein direktes analoges Signal
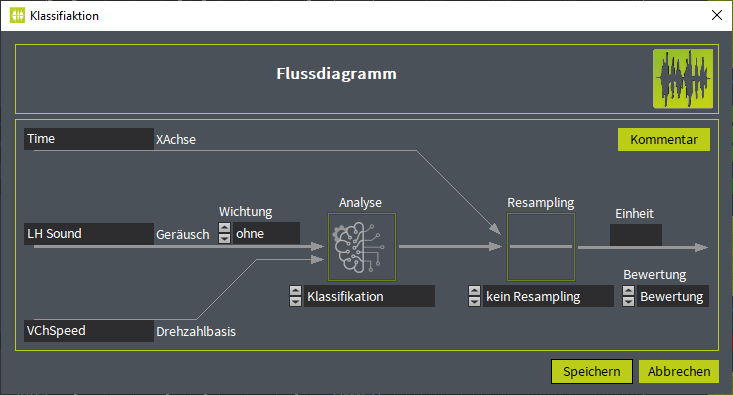 Definition der Berechnung eines jeden Merkmals im Flussdiagramm
Definition der Berechnung eines jeden Merkmals im Flussdiagrammlinks im Bild: Eingangskanal (Messsignal) mit aufgenommenen Geräusch
- Für eine Pegelanalyse eines Mikrofonsignals empfiehlt sich eine "A"-Wichtung.
- es folgt die Signalanalyse (im Beispiel die Klassifikation), die hier ausgewählt und parametriert werden kann.
- optionales Resampling, dabei wird die…
Artificial Intelligence
CARoLINE can be equipped with optional AI connection interfaces.
→ Read more about AI for Sound Analysis
Modulation analysis of exterior mirrors
The so-called modulation analysis is intended to find out how strongly a certain frequency fluctuates in the course of a selected movement - for example, during the unfolding movement of the vehicle exterior mirror. If this fluctuation around the determined centre frequency is too strong, this can be perceived as an unpleasant lyre.
The results of a modulation analysis can look like this, for example:
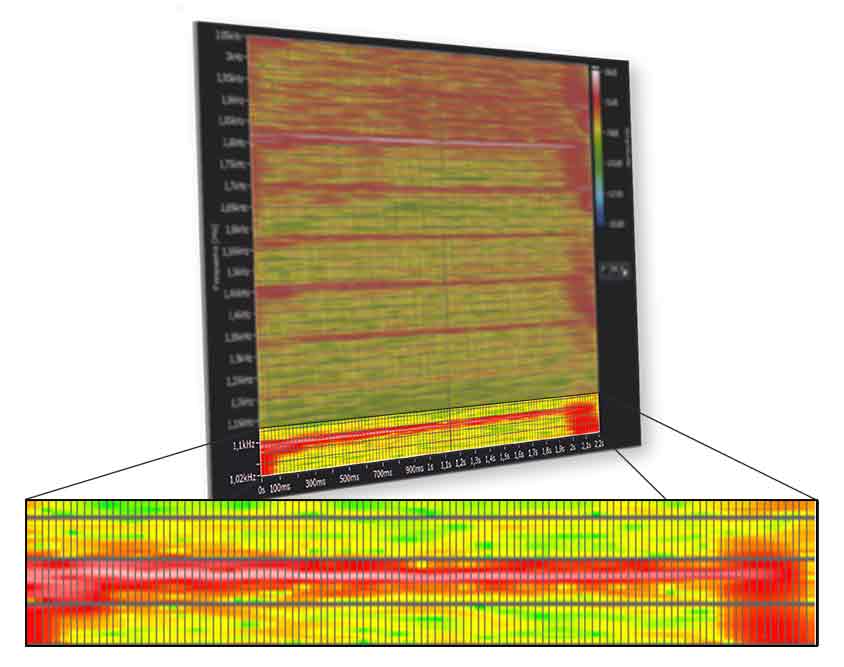
fcenter = 1087 Hz , f fluc,p = 43 Hz
f fluc = 19 Hz ⇒ Modulation test OK
The centre frequency fcenter sets the value for the permitted frequency fluctuations f fluc,p, f fluc for the fluctuation that actually occurred. The fluctuations that occurred with this exterior mirror are within the permitted limit.
Modulation tests can also be determined for frequencies that continuously shift towards higher or lower frequencies over the test time. It does not matter whether this is a linear process or not. Only the calculation method differs here.
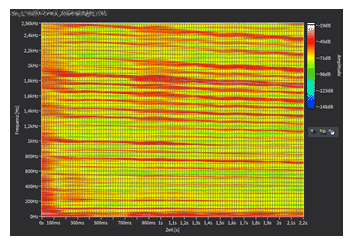
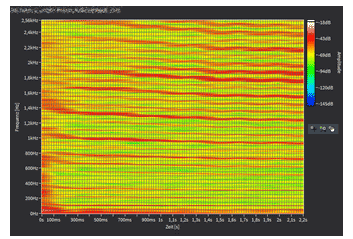
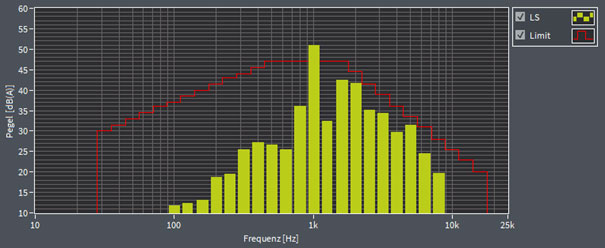
Third-octave analysis on side mirrors
With the so-called third-octave analysis, conspicuous frequency ranges can be determined very quickly and monitored using limits. In addition, the third-octave analysis serves as a basis for determining the tonality of the mirror, which can be used to test whether it causes a melodious or disturbing noise.
In this third-octave analysis, the third octave of the frequency 1000 Hz exceeds the set limit and thus also the set tolerance limits.
These acoustic analysis procedures are used for quality assurance of complex assemblies that become conspicuous in the end-of-line test. Assembly errors or susceptible drive systems can be quickly localised.
Typical acoustic methods with CARoLINE
- evaluation of single or combined frequency bands, including octave or one-third octave analysis
- order analysis, also combined
- rotary speed analysis from the resonance signal or ripple power signal of the motor to be used in the order analysis or for modulation analysis
- statistical analysis for process control
 Demande
Demande